We havelearnedsome ofthe numericalmethodsin the P2 course, when we used the trapezium rule to approximate the area under a curve in thex-O-y plane. The trapezium rule divides the area into n parts. For each part we calculate the area of the corresponding trapezium to approximate the area of the bounded region. Thenwe summarise the results to approach the total area which is the value ofthe definiteintegral.
Now we try to solve the rooting problem of a function in numerical wayFirst of alllets learn how to locate roots using the change-of-sign rule Hereisthetheorem:
If the function f(x) is continuous in the
interval [a,b]and f(a)and f(b) have opposite signs, then f(x) has at least one rootxwhich satisfiesa
The special cases we need to pay attention to are:

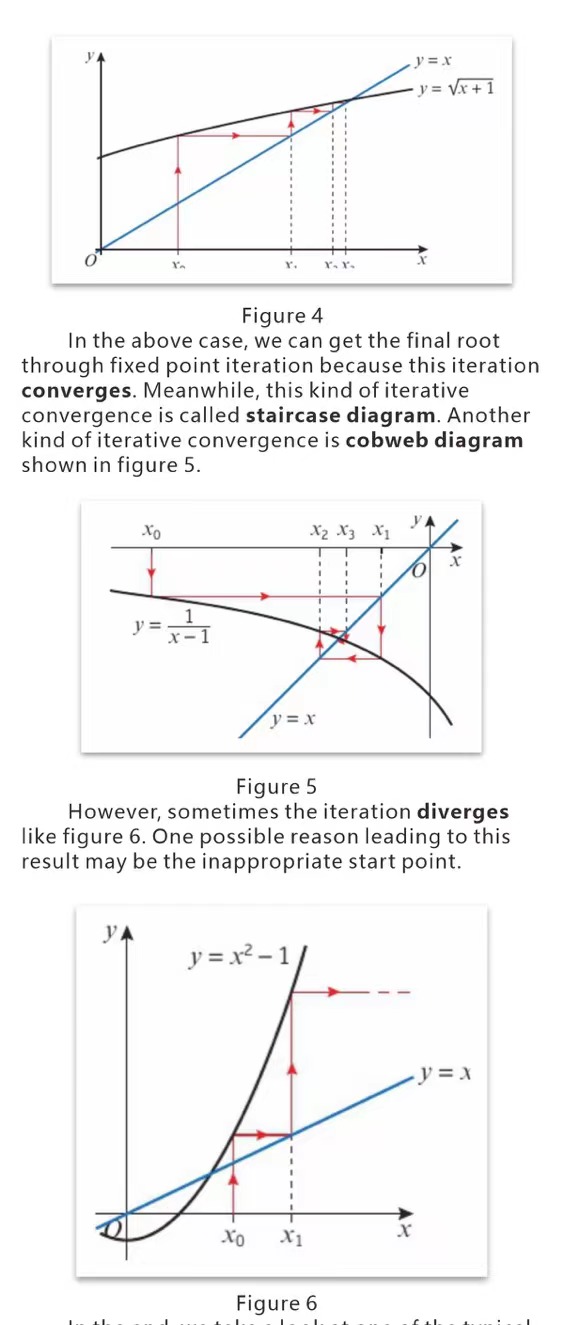
Now that we have locate the root ofthe
function into a certain intervalnextwe make efforts to use numerical method toapproximate the root.
If we want to find the roots ofa fucntionsuch as f(x)=0,we could rewrite the equation as g(x)=x.Then it is equivalent to finding the x- coordinate of the intersection point of the two curves with the equations y=g(x) andy=x. Therefore, like fugure 4 shows, if we set a start valuex,then followtheiterativeformulaxn+1=g(xn) we will get closer and closer to the intersection point. The way we approches the root of the function is called fixed point iteration which is a kind ofnumerical method.