要说AS经济中,哪个知识点在考试中出现的频率比较高, Price Elasticity of Demand(PED)需求价格弹性一定是其中之一。
PED的重要性就在于,它和其他很多的经济学知识点都有着紧密的关联,因此,学好这个知识点至关重要。
今天,小编就来给大家讲讲这个AS微观经济部分的内容。
1. PED的定义与公式
2. 举例说明PED的计算方法
3. 弹性需求与非弹性需求的区别与特征
4. PED与Revenue公司收入、Price discrimination价格歧视与Tax incidence税收归宿之间的关联。
Definition 定义与公式
定义Definition:
Price elasticity of demand (PED) measures the responsiveness of demand after a change in price.
公式:

Examples of PED 例子(计算过程)
1. If price increases by 10% and demand for CDs fell by 20%
Then PED = -20/10 = -2.0
2. If the price of petrol increased from 130p to 140p and demand fell from 10,000 units to 9,900
% change in Q.D = (-100/10,000) *100 = – 1%
% change in price 10/130 ) * 100= 7.7%
Therefore PED = – 1/7.7 = -0.13
Price elastic demand and inelastic demand
弹性需求和非弹性需求
Price Elastic Demand 弹性需求
Definition: Demand is price elastic if a change in price leads to a bigger % change in demand; therefore the PED will, therefore, be greater than 1.
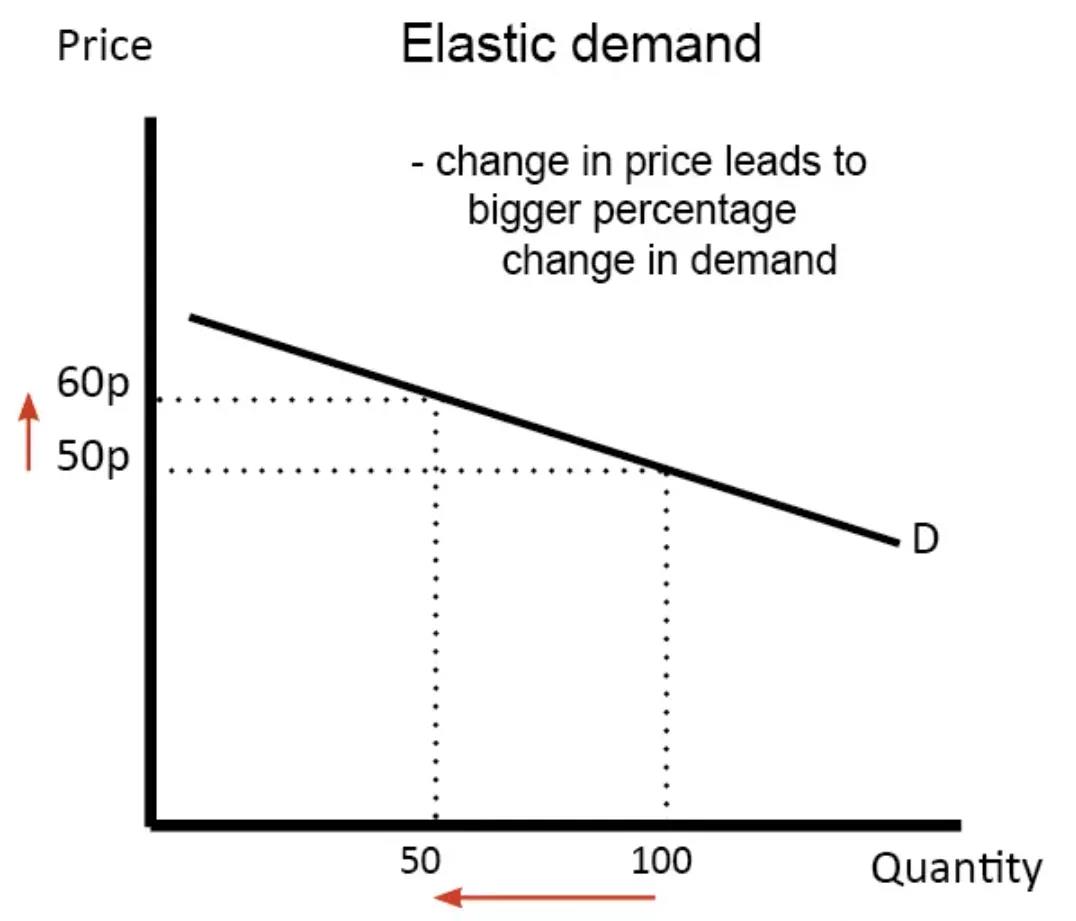
Goods which are elastic, tend to have some or all of the following characteristics.
1. They are luxury goods, e.g. sports cars
2. They are expensive and a big % of income e.g. sports cars and holidays
3. Goods with many substitutes and a very competitive market. E.g. if Sainsbury’s put up the price of its bread there are many alternatives, so people would be price sensitive.
4. Bought frequently
Price Inelastic Demand 非弹性需求
These are goods where a change in price leads to a smaller % change in demand; therefore PED <1 e.g. – 0.5
Inelastic demand PED <1 – Perfectly inelastic PED =0
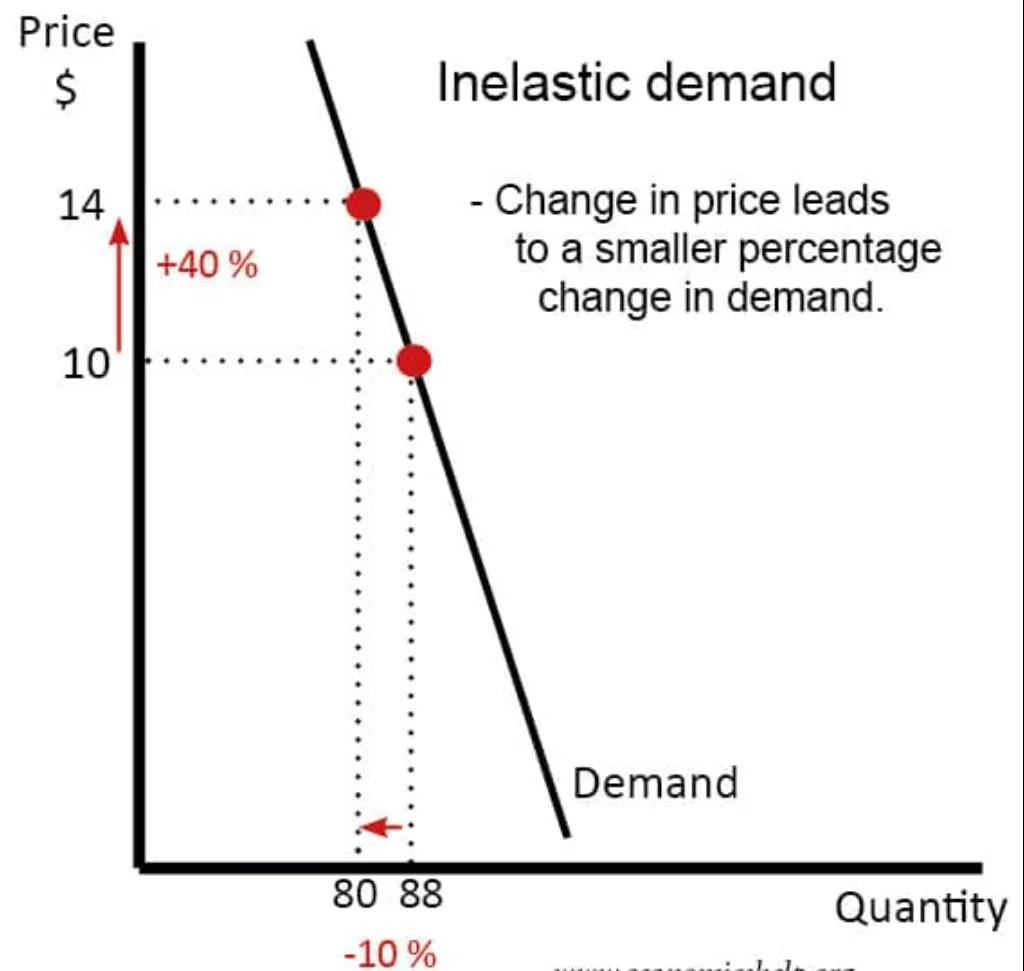
Goods which are inelastic tend to have some or all of the following features:
1. They have few or no close substitutes, e.g. petrol, cigarettes.
2. They are necessities, e.g. if you have a car, you need
3. to keep buying petrol, even if price of petrol increases
4. They are addictive, e.g. cigarettes.
5. They cost a small % of income or are bought infrequently.
In the short term, demand is usually more inelastic because it takes time to find alternatives.
If the price of chocolate increased demand would be inelastic because there are no alternatives, however, if the price of Mars increased there are close substitutes in the form of other chocolate, therefore, demand will be more elastic.
PED与其他知识点的关联
1. Revenue PED与Revenue公司收入的关系
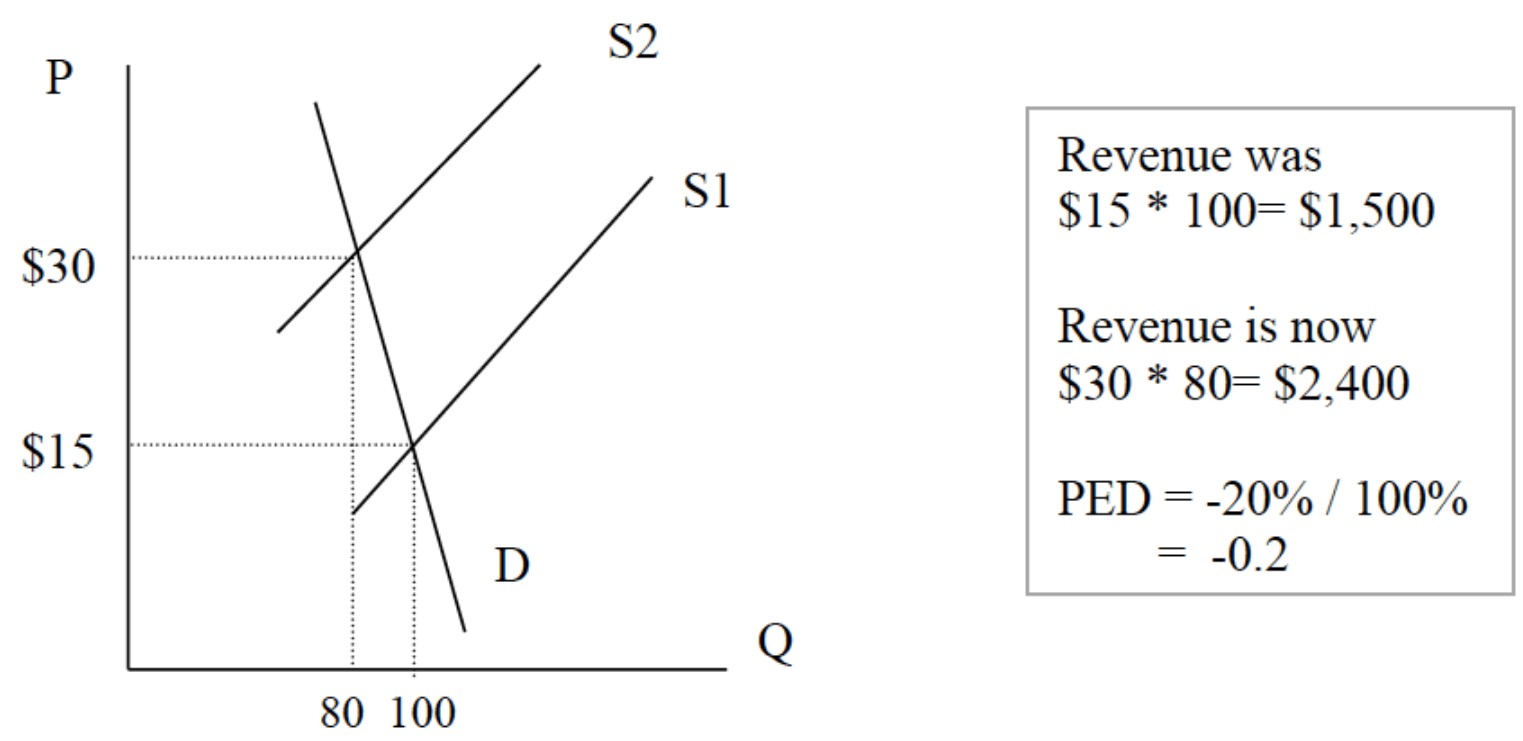
If demand is inelastic then increasing the price can lead to an increase in revenue. This is why OPEC try to increase the price of oil.
如果是非弹性需求,涨价会使得公司revenue增加,这就是为什么石油输出国家组织想要提高油价。
Graph showing increase in Revenue following increase in price
If demand is elastic, firms would be unlikely to increase revenue as this could lead to a fall in revenue. Instead, they could try advertising to increase brand loyalty and make demand more inelastic
如果是弹性需求,公司一般会选择降价,而不是涨价,来增收。除此之外,公司还会通过广告等营销手段,提高品牌忠诚度,以此来降低需求的弹性。
2. PED and Price discrimination. PED与价格歧视的关系
Some people pay higher prices for tickets for trains because their demand is more inelastic.
有些人愿意高价买票,是因为他们的需求缺乏弹性。
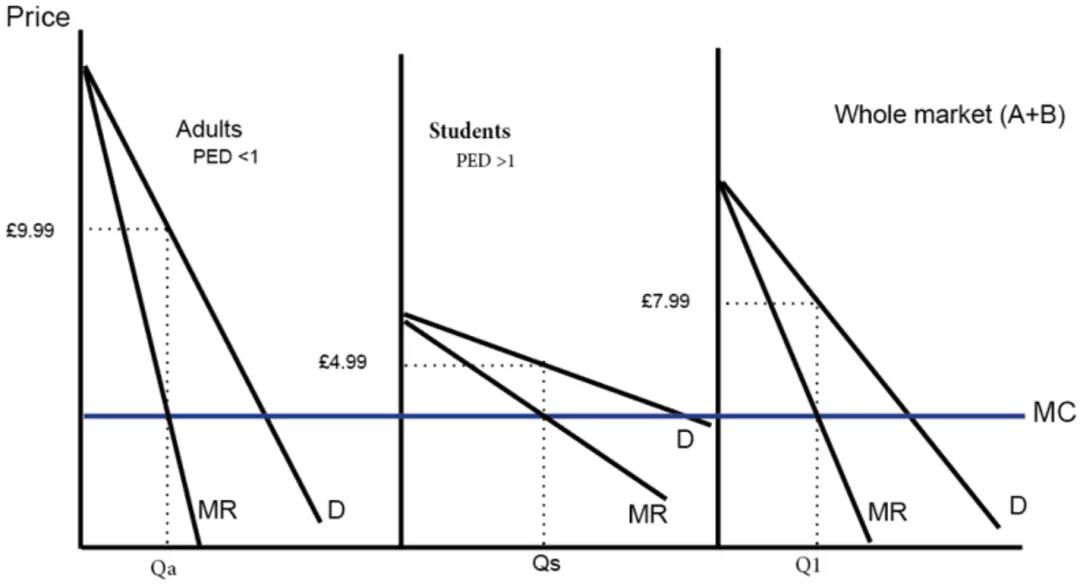
Adults (with more inelastic demand) face higher prices. Students with more elastic demand get lower price.
例如,大部分成年人由于有稳定收入,即使价格高也会购买,因此他们的需求弹性较低。而学生群体,由于大多没有稳定收入,其需求弹性就较高(价格高就不买)。
因此,可以根据不同群体具有不同弹性的特征,可以针对不同群体实行不同的价格,以增加total revenue。
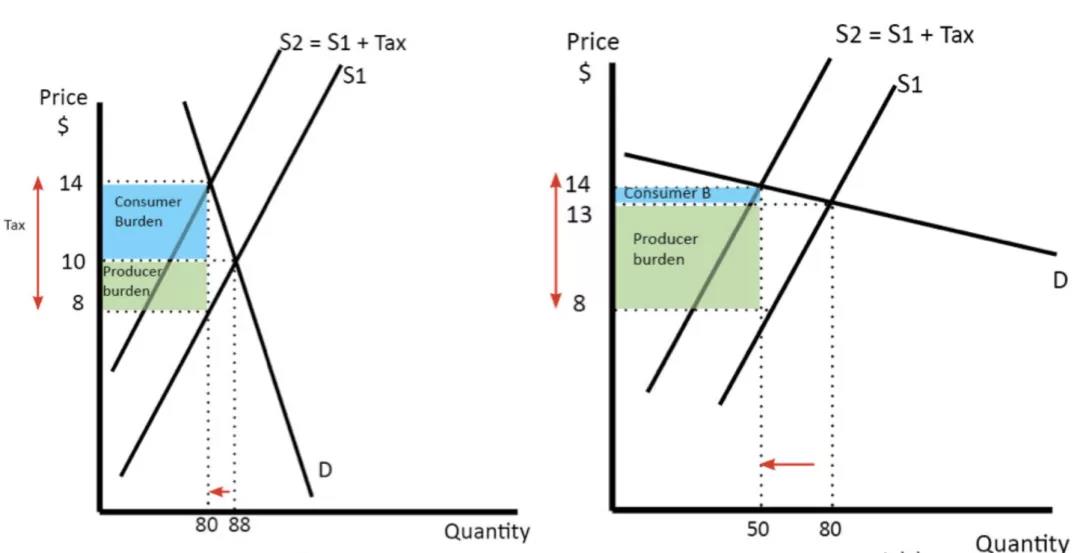
3. PED and tax incidence. PED与税收归宿
If demand is price inelastic, then a higher tax will lead to higher prices for consumers (e.g. tobacco tax). The tax incidence will mainly be borne by consumers.
当需求弹性较低,消费者对价格不敏感,税收(Indirect tax间接税)大多由消费者承担。
If demand is price elastic, firms will face a bigger burden, and consumers will have a lower tax burden.
当需求弹性较高,消费者对价格敏感,税收(Indirect tax间接税)大多由商家者承担。
如果你想了解更多A-level课程,留学规划或者有任何疑问,欢迎联系新航道重庆学校。
新航道重庆学校官网:cq.xhd.cn
新航道重庆学校官方电话:400-185-9090
推荐阅读:
一起来唠唠出国留学英国后的那些“坑”,用自己的血泪教训给大家排个雷~
关于QS排名前100的澳洲院校的花费大全来啦,想去这些学校的小伙伴们有没有准备好钱包呀?